Table of Contents
What is In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)?
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is an assisted reproductive technology (ART) used to help couples and individuals who are struggling with infertility. The procedure involves retrieving eggs from a woman’s ovaries and fertilizing them with sperm in a laboratory. Once fertilized, the embryos are cultured for a few days before one or more are transferred to the woman’s uterus to establish a pregnancy.
IVF offers hope to couples who have not been able to conceive naturally due to various medical conditions. By facilitating fertilization outside the body, IVF bypasses the potential barriers that may prevent conception in natural pregnancies.
Why is IVF Treatment Needed?
Fertility challenges can be caused by a range of factors that affect both men and women. IVF is often used when other less invasive treatments, such as fertility medications or intrauterine insemination (IUI), have not been successful. Here are some of the most common conditions for which IVF is recommended:
1. Damage or Blockage in the Fallopian Tubes
The fallopian tubes are the site where sperm meets the egg for fertilization in a natural pregnancy. If the fallopian tubes are damaged or blocked due to injury, infection, or surgery, the egg and sperm cannot meet, leading to infertility. IVF bypasses the fallopian tubes altogether by allowing fertilization to occur in a controlled laboratory environment.
2. Ovulation Disorders
Ovulation is the process where a mature egg is released from the ovary. For some women, ovulation is irregular or absent, making it impossible to conceive naturally. IVF, in combination with medications that stimulate the ovaries to produce eggs, is an effective treatment for women with ovulation disorders.
3. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that normally lines the uterus, called the endometrium, grows outside the uterus. This can lead to pain and fertility issues. Endometriosis affects egg quality and the ability of an embryo to implant in the uterus. IVF treatment can bypass some of these issues by retrieving healthy eggs and transferring embryos directly into the uterus, increasing the chances of a successful pregnancy.
4. Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop in the uterus and can affect fertility. Fibroids can interfere with the implantation of the embryo in the uterus, leading to difficulty in becoming pregnant or maintaining a pregnancy. IVF can help women with fibroids conceive by creating healthy embryos that are transferred into the uterus after fibroids have been treated.
5. Poor Egg Quality
The quality of a woman’s eggs plays a critical role in successful conception and pregnancy. Poor egg quality, often seen in women over 35, can result in chromosomal abnormalities that hinder fertilization or lead to miscarriages. IVF allows fertility specialists to assess the quality of eggs and embryos, selecting only the healthiest for implantation, thereby increasing the chances of a successful pregnancy.
6. Age-Related Fertility Decline
Women over 40 often face a significant decline in fertility due to the aging of their eggs. As the number and quality of eggs decrease with age, the chances of natural conception become slimmer. IVF helps women over 40 achieve pregnancy by using fertility medications to stimulate the ovaries, increasing the chances of retrieving healthy eggs. In cases where egg quality is severely compromised, donor eggs can also be used in IVF to facilitate a healthy pregnancy.
7. Male Factor Infertility
Infertility isn’t solely a female issue; male factor infertility is responsible for nearly half of all infertility cases. Common male fertility issues include low sperm count, poor sperm motility, or abnormal sperm morphology. IVF can address male infertility by combining it with a technique known as Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI), in which a single healthy sperm is injected directly into the egg for fertilization.
8. Inability of Sperm to Survive in Cervical Mucus
In some cases, sperm may struggle to survive in the cervical mucus, which acts as a barrier between the vagina and the uterus. Abnormal cervical mucus can impair sperm motility and prevent them from reaching the egg. IVF circumvents this problem by directly introducing sperm to the eggs in a laboratory setting.
9. Genetic Disorders
Couples with a history of genetic disorders may seek IVF treatment to prevent passing these conditions on to their children. IVF allows for preimplantation genetic testing (PGT), in which embryos are screened for genetic abnormalities before being transferred to the uterus. This ensures that only healthy embryos are implanted, reducing the risk of genetic diseases in the offspring.
10. Unexplained Infertility
In some cases, despite comprehensive testing, the cause of infertility remains unknown. This is referred to as unexplained infertility. For couples experiencing unexplained infertility, IVF can be a valuable solution, as it offers a more controlled environment for fertilization and embryo development. IVF treatments can improve the chances of pregnancy for couples who have not found success with other fertility treatments.
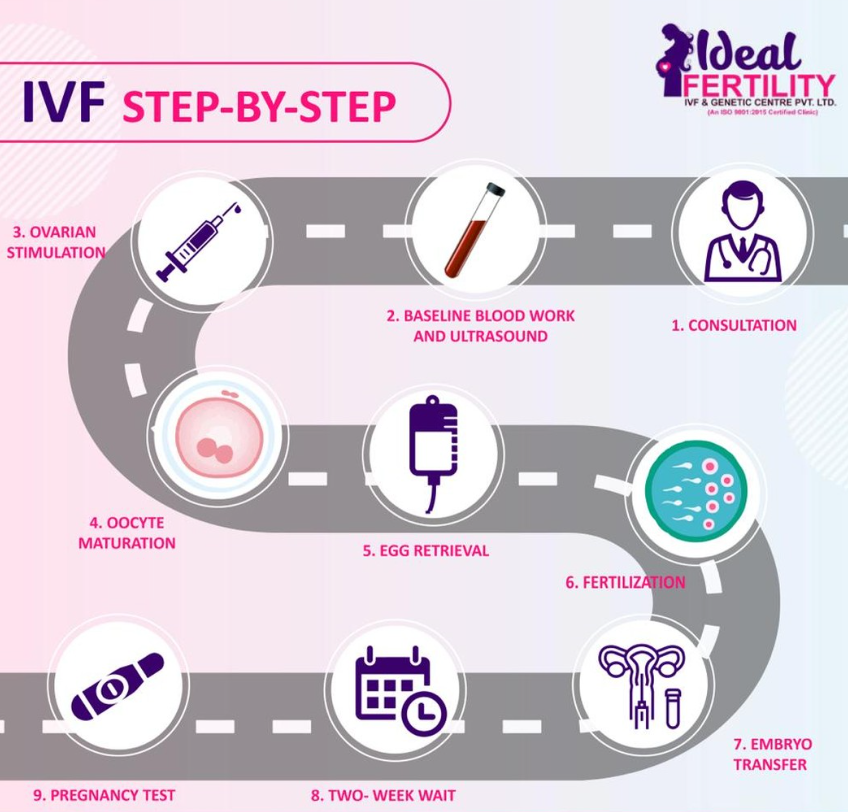
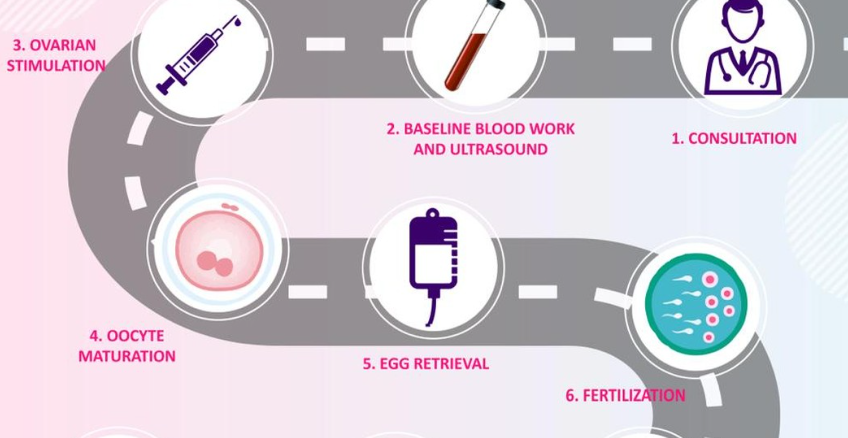
IVF Procedure: Step-by-Step Process
The IVF process involves several stages, each of which is carefully monitored by fertility specialists to maximize the chances of success. Here’s a brief overview of the steps involved in IVF treatment:
1. Ovarian Stimulation
The first step in IVF is ovarian stimulation, where fertility medications are administered to the woman to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. The goal is to retrieve as many mature eggs as possible for fertilization.
2. Egg Retrieval
Once the eggs have matured, they are retrieved from the ovaries through a minor surgical procedure. This is typically done under sedation to minimize discomfort.
3. Sperm Collection and Fertilization
A sperm sample is collected from the male partner or a sperm donor. The eggs and sperm are then combined in a laboratory dish to allow fertilization. In cases where male factor infertility is present, ICSI may be used to inject a single sperm into each egg.
4. Embryo Culture
Once fertilization occurs, the embryos are monitored for several days as they develop in the laboratory. Fertility specialists assess the quality of the embryos and select the best ones for transfer.
5. Embryo Transfer
After the embryos have developed for a few days, one or more are transferred to the woman’s uterus. This is a simple procedure performed under ultrasound guidance. If successful, the embryo will implant in the uterine lining, resulting in pregnancy.
6. Pregnancy Testing
A blood test is conducted about two weeks after the embryo transfer to determine whether pregnancy has occurred. If the test is positive, the pregnancy will be monitored closely to ensure healthy development.
Advancements in IVF Technology
As IVF technology continues to evolve, new techniques are being developed to improve success rates and make the process more efficient.
A. Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
PGT allows fertility specialists to screen embryos for chromosomal abnormalities before implantation, reducing the risk of miscarriage or genetic disorders. This is particularly beneficial for older women or couples with a history of genetic diseases.
B. Non-Invasive Testing
Non-invasive preimplantation genetic testing (niPGT) is an emerging technology that allows for the analysis of embryos without damaging them. By testing the culture media surrounding the embryos, fertility specialists can identify genetic abnormalities while preserving embryo viability.
C. Cryopreservation
Advances in cryopreservation have made it possible to freeze eggs, sperm, and embryos for future use. This is particularly useful for individuals who wish to preserve their fertility for medical or personal reasons.
Conclusion
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) has revolutionized the treatment of infertility, offering hope to millions of individuals and couples who struggle to conceive. With advancements in technology and a deep understanding of reproductive health, IVF continues to evolve, improving success rates and making parenthood a reality for many. Whether addressing male or female infertility, age-related decline, or genetic concerns, IVF remains one of the most effective and widely used fertility treatments available today.