Table of Contents
In the domain of modern healthcare, the Fetal Medicine Unit (FMU) plays a pivotal role in ensuring the health and well-being of both expectant mothers and their unborn babies. Specializing in the comprehensive evaluation, diagnosis, and management of fetal conditions, the FMU serves as a cornerstone of advanced prenatal care. With cutting-edge technology and expert medical teams, the FMU addresses complex cases, from routine screenings to high-risk pregnancies, offering hope and reassurance to families worldwide.
This article explores the concept of the FMU, its role in healthcare, the specialized services it offers, and how it is transforming maternal-fetal medicine.
Understanding FMU: What is the Fetal Medicine Unit?
The Fetal Medicine Unit (FMU) is a specialized division within maternity and obstetric care that focuses on the diagnosis and management of fetal conditions during pregnancy. It bridges the gap between obstetrics, pediatrics, and neonatal care by providing advanced diagnostic and therapeutic interventions for both the mother and fetus.
The FMU is staffed by highly trained fetal medicine specialists, obstetricians, sonographers, genetic counselors, and neonatal experts. Together, they ensure that pregnancies are monitored and managed with the highest standard of care.
Key Roles and Objectives of the FMU
The primary objective of the FMU is to optimize outcomes for both mother and baby. This is achieved through a combination of early diagnosis, risk assessment, and targeted interventions.
- Early Detection of Fetal Anomalies
- The FMU specializes in detecting structural, genetic, and chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus.
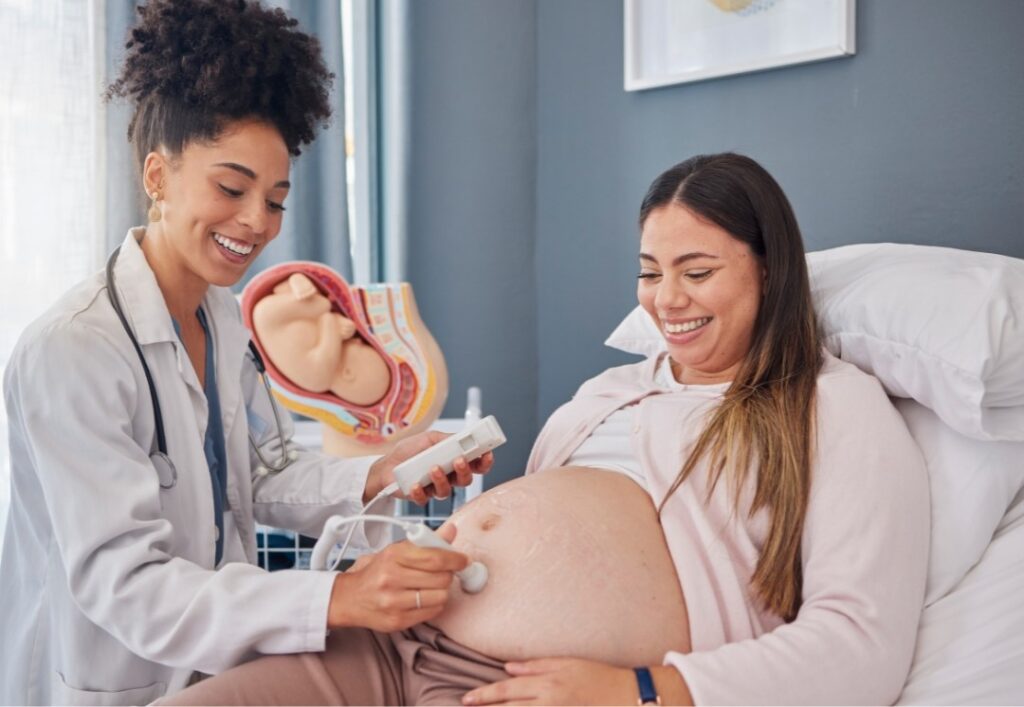
- Advanced imaging techniques, like high-resolution ultrasound and fetal MRI, allow detailed evaluation of fetal anatomy.
- Risk Assessment for High-Risk Pregnancies
- For mothers with pre-existing medical conditions (e.g., diabetes, hypertension) or a history of pregnancy complications, the FMU conducts comprehensive risk assessments.
- It also monitors conditions like pre-eclampsia and placental insufficiency.
- Multidisciplinary Approach to Care
- The FMU works collaboratively with specialists in cardiology, neurology, genetics, and neonatology to provide holistic care.
- Parental Counseling and Support
- Parents are provided with detailed information about their baby’s condition, possible outcomes, and treatment options.
- Emotional and psychological support is an integral part of FMU services.
Advanced Diagnostic Tools in the FMU
The FMU relies on state-of-the-art technology for precise diagnosis and monitoring of fetal health.
- Ultrasound Scans
- First Trimester Screening: Evaluates nuchal translucency (NT) and other markers to assess the risk of chromosomal abnormalities like Down syndrome.
- Anomaly Scan: Conducted between 18-22 weeks to detect structural anomalies.
- Growth Scans: Monitor fetal growth and amniotic fluid levels.
- Fetal Echocardiography
- A specialized ultrasound to assess the fetal heart, particularly in pregnancies with a risk of congenital heart defects.
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
- A blood test analyzing fetal DNA from the mother’s bloodstream to detect chromosomal abnormalities with high accuracy.
- Fetal MRI
- Used in complex cases to provide detailed imaging of fetal organs, particularly the brain and spine.
- Amniocentesis and Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
- Invasive procedures performed to obtain fetal cells for genetic analysis, providing definitive diagnoses for conditions like trisomy 21 or cystic fibrosis.
Therapeutic Interventions in the FMU
Beyond diagnosis, the FMU plays a critical role in managing and treating fetal conditions during pregnancy.
- Fetal Surgery
- Some FMUs are equipped to perform in-utero surgeries, such as repairing spina bifida or treating twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) using laser ablation.
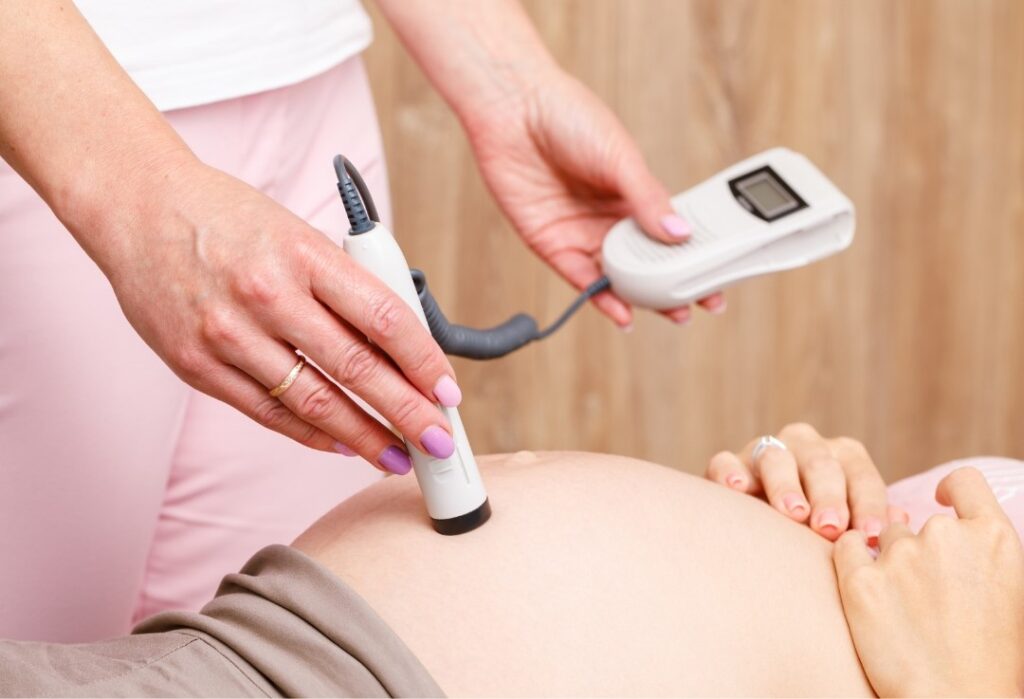
- Fetal Blood Transfusions
- For cases of severe fetal anemia, the FMU can perform blood transfusions directly into the umbilical cord or fetal vein.
- Management of Multiple Pregnancies
- Twin and higher-order pregnancies are carefully monitored to prevent complications like TTTS or preterm labor.
- Medications
- Certain conditions, like fetal arrhythmias, can be managed with medications administered to the mother, which cross the placenta to treat the fetus.
High-Risk Pregnancy Management
For women with high-risk pregnancies, the FMU provides a tailored care plan to ensure the best possible outcomes.
- Fetal Surgery
- Some FMUs are equipped to perform in-utero surgeries, such as repairing spina bifida or treating twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) using laser ablation.
- Fetal Blood Transfusions
- For cases of severe fetal anemia, the FMU can perform blood transfusions directly into the umbilical cord or fetal vein.
- Management of Multiple Pregnancies
- Twin and higher-order pregnancies are carefully monitored to prevent complications like TTTS or preterm labor.
- Medications
- Certain conditions, like fetal arrhythmias, can be managed with medications administered to the mother, which cross the placenta to treat the fetus.
The Role of Genetic Counseling in the FMU
Genetic counseling is an integral component of the FMU, particularly for families with a history of genetic disorders or abnormal prenatal screening results.
- Explaining Test Results
- Counselors help parents understand the implications of genetic tests and discuss options for further testing or management.
- Family History Evaluation
- Detailed family histories are analyzed to assess the risk of inherited conditions.
- Support in Decision-Making
- Genetic counselors guide families in making informed decisions, whether it’s about continuing a pregnancy or exploring treatment options.
How the FMU Supports Neonatal Outcomes
The FMU’s work doesn’t end with delivery. Its role extends to ensuring smooth transitions for babies who require specialized neonatal care.
- Delivery Planning
- For pregnancies with anticipated complications, the FMU collaborates with neonatal teams to plan for delivery at facilities equipped with NICUs.
- Postnatal Interventions
- Some conditions, like congenital heart defects, require immediate surgical interventions after birth, which are coordinated by the FMU.
- Long-Term Follow-Up
- Babies diagnosed with conditions in utero are often enrolled in long-term follow-up programs to monitor their growth and development.
The Emotional Support Provided by FMUs
Pregnancies involving fetal complications can be emotionally taxing. The FMU offers a supportive environment to help parents navigate these challenges.
- Counseling Services: Available to help parents cope with stress, grief, or difficult decisions.
- Support Groups: Many FMUs connect families with others who have faced similar situations, fostering a sense of community.
Global Trends in FMU Services
- Technological Advancements:
- Innovations in imaging and minimally invasive techniques are expanding the capabilities of FMUs worldwide.
- Increased Access:
- Countries are investing in FMUs to improve maternal and fetal health outcomes, particularly in underserved areas.
- Holistic Care Models:
- The integration of mental health support, nutrition counseling, and genetic services ensures comprehensive care for families.
Challenges and Future Directions
- Resource Limitations:
- Many regions lack access to FMUs, creating disparities in maternal-fetal care.
- Training and Expertise:
- Expanding the pool of trained fetal medicine specialists is crucial to meet growing demand.
- Research and Innovation:
- Continued research is needed to develop new treatments for fetal conditions and improve outcomes.
Conclusion
The Fetal Medicine Unit is a beacon of hope in modern healthcare, offering advanced diagnostics, therapeutic interventions, and compassionate care for high-risk pregnancies. Its multidisciplinary approach ensures that both mother and baby receive the best possible care, from conception to delivery and beyond.
As technology advances and access to specialized care improves, FMUs will continue to play a transformative role in maternal and fetal health, shaping the future of prenatal care and ensuring healthier beginnings for generations to come.